Core Concepts
Core Concepts of Flux.
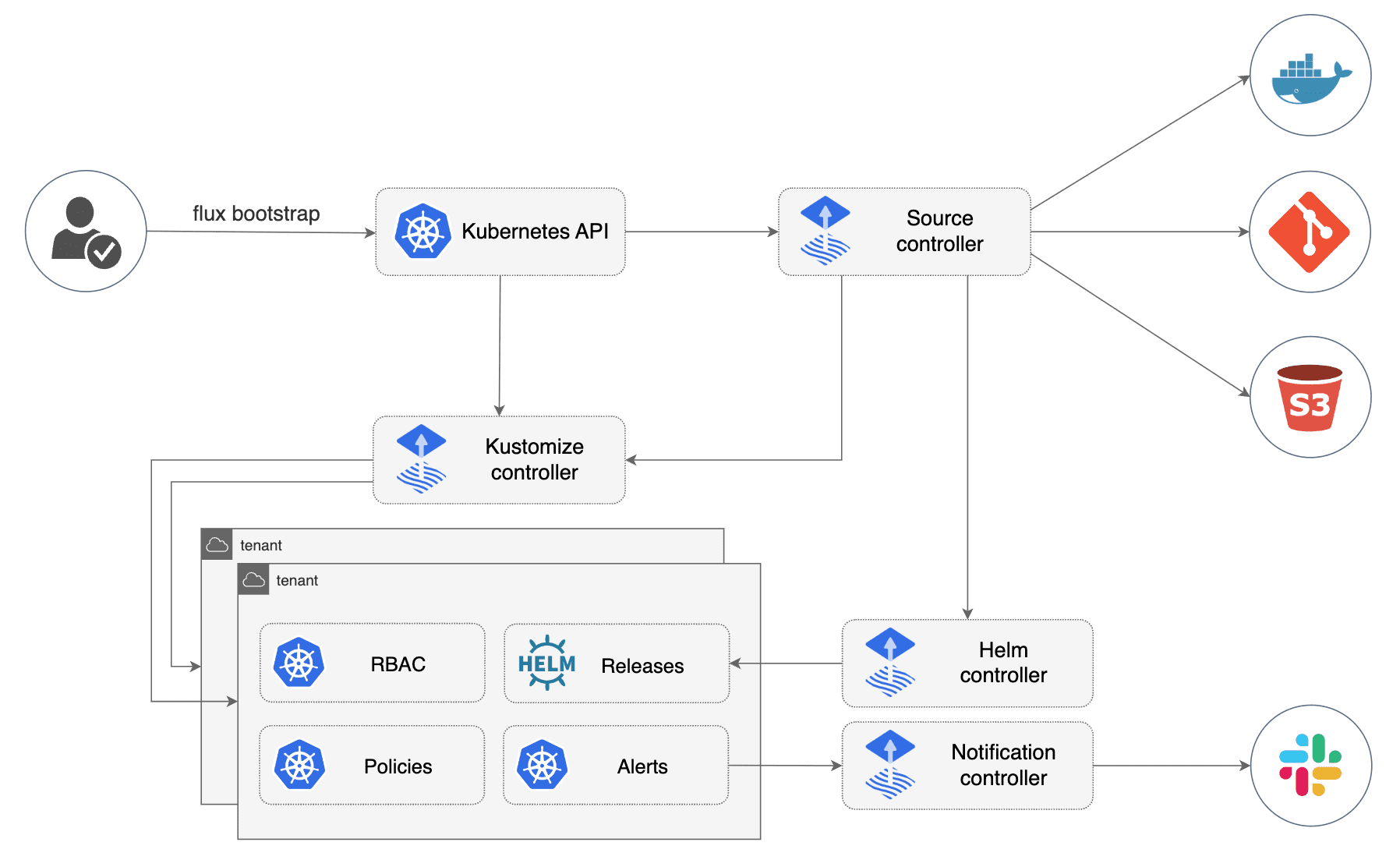
Flux is a tool for keeping Kubernetes clusters in sync with sources of configuration (like Git repositories), and automating updates to configuration when there is new code to deploy.
Flux is built from the ground up to use Kubernetes' API extension system, and to integrate with Prometheus and other core components of the Kubernetes ecosystem. Flux supports multi-tenancy and support for syncing an arbitrary number of Git repositories.
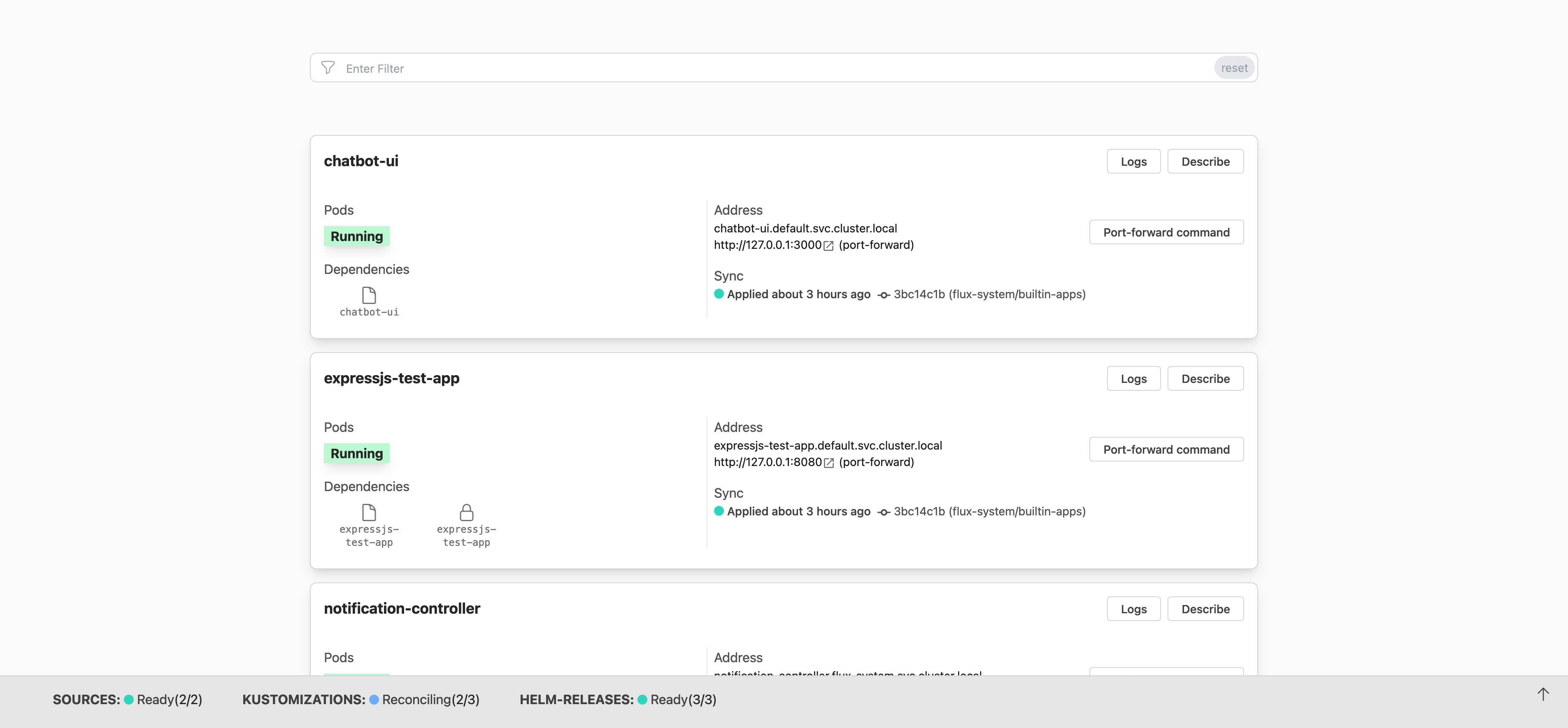
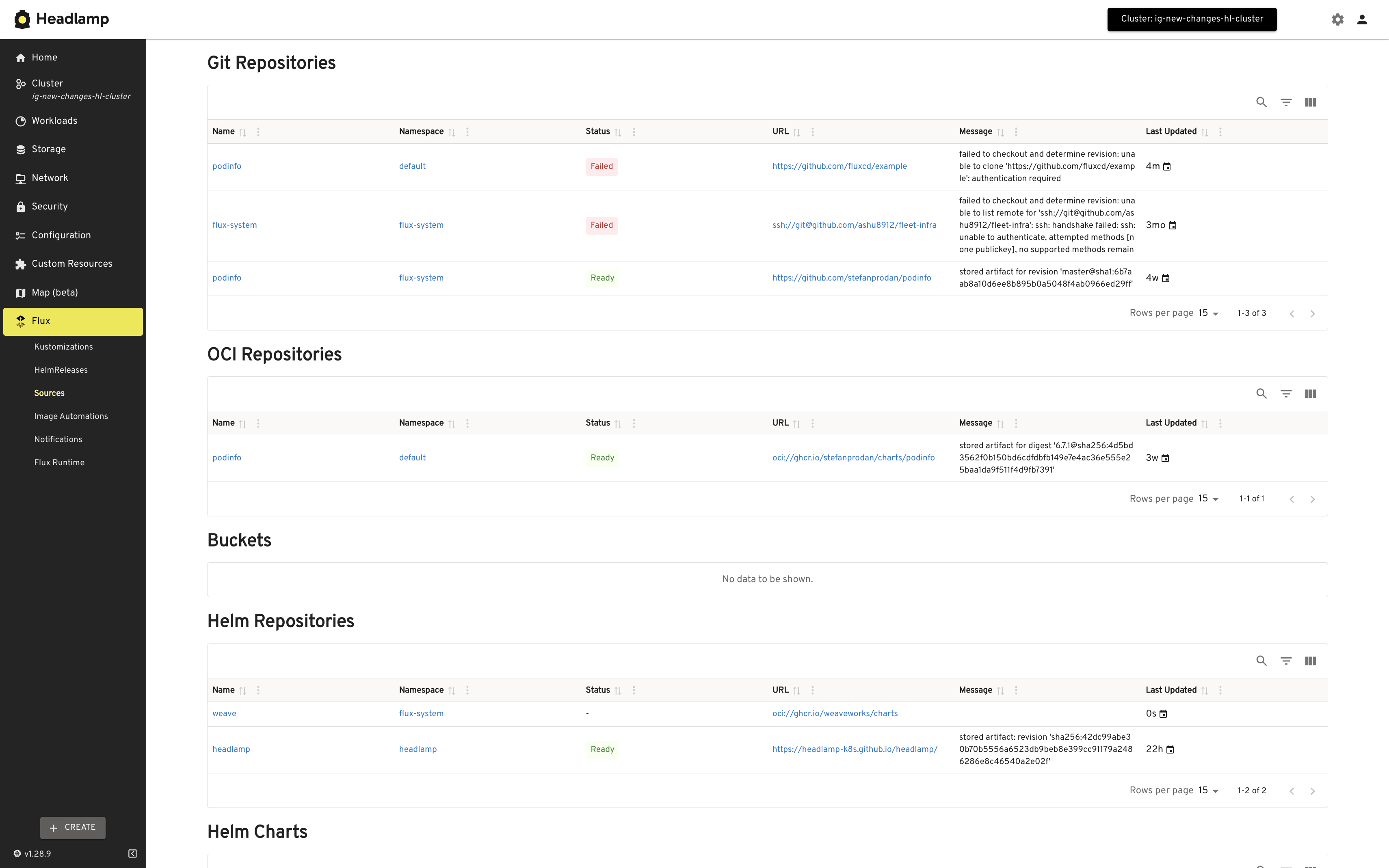
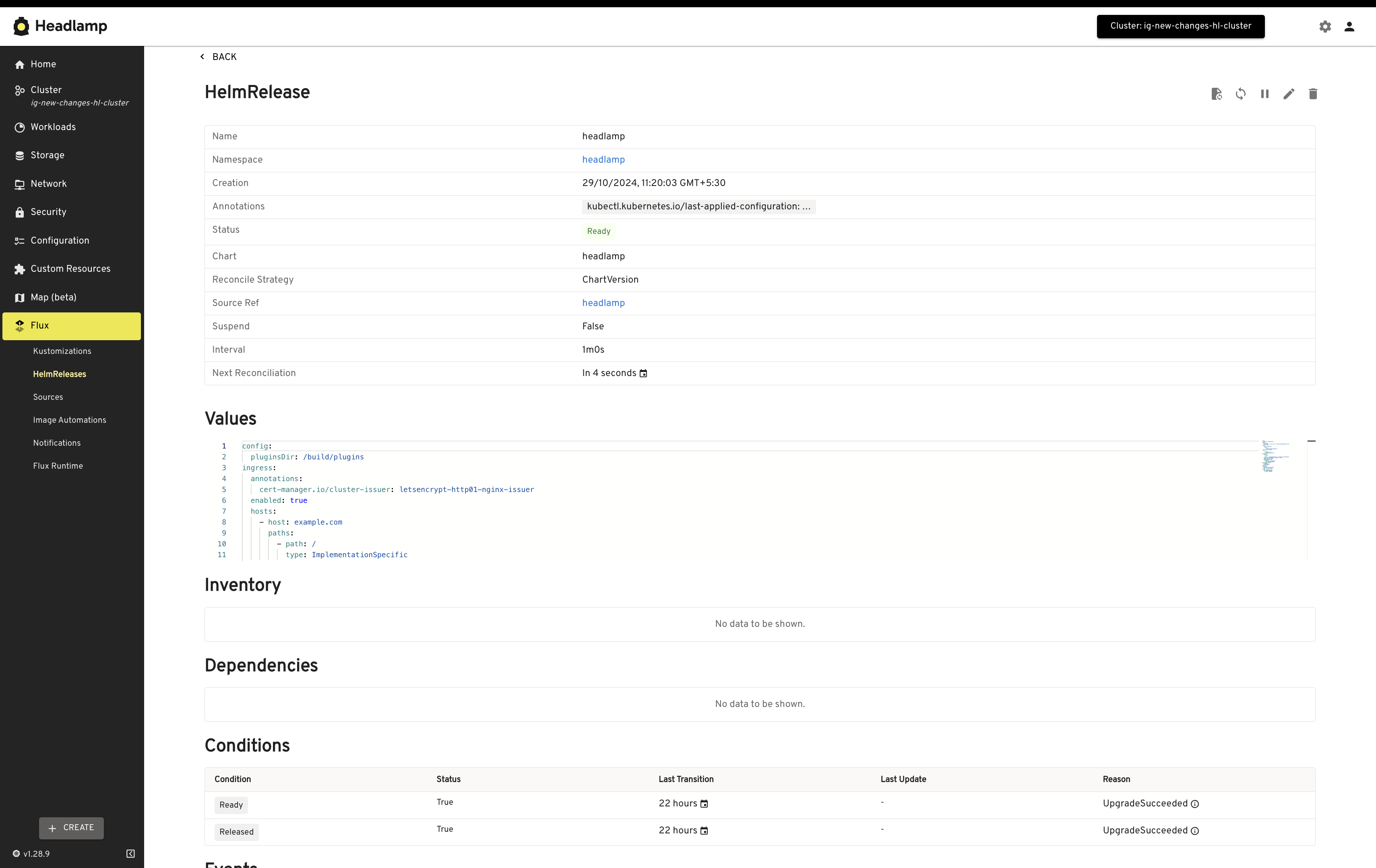
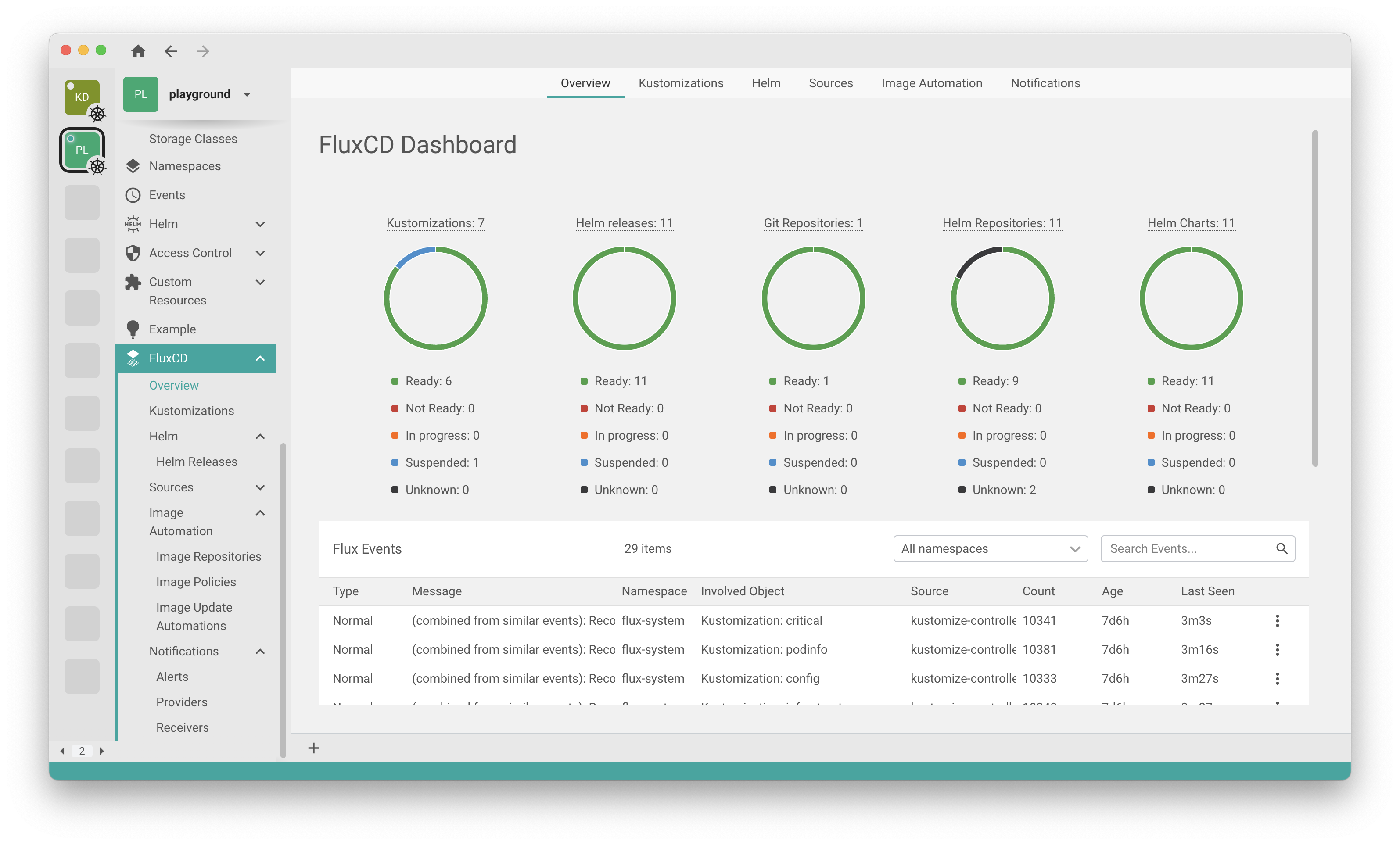
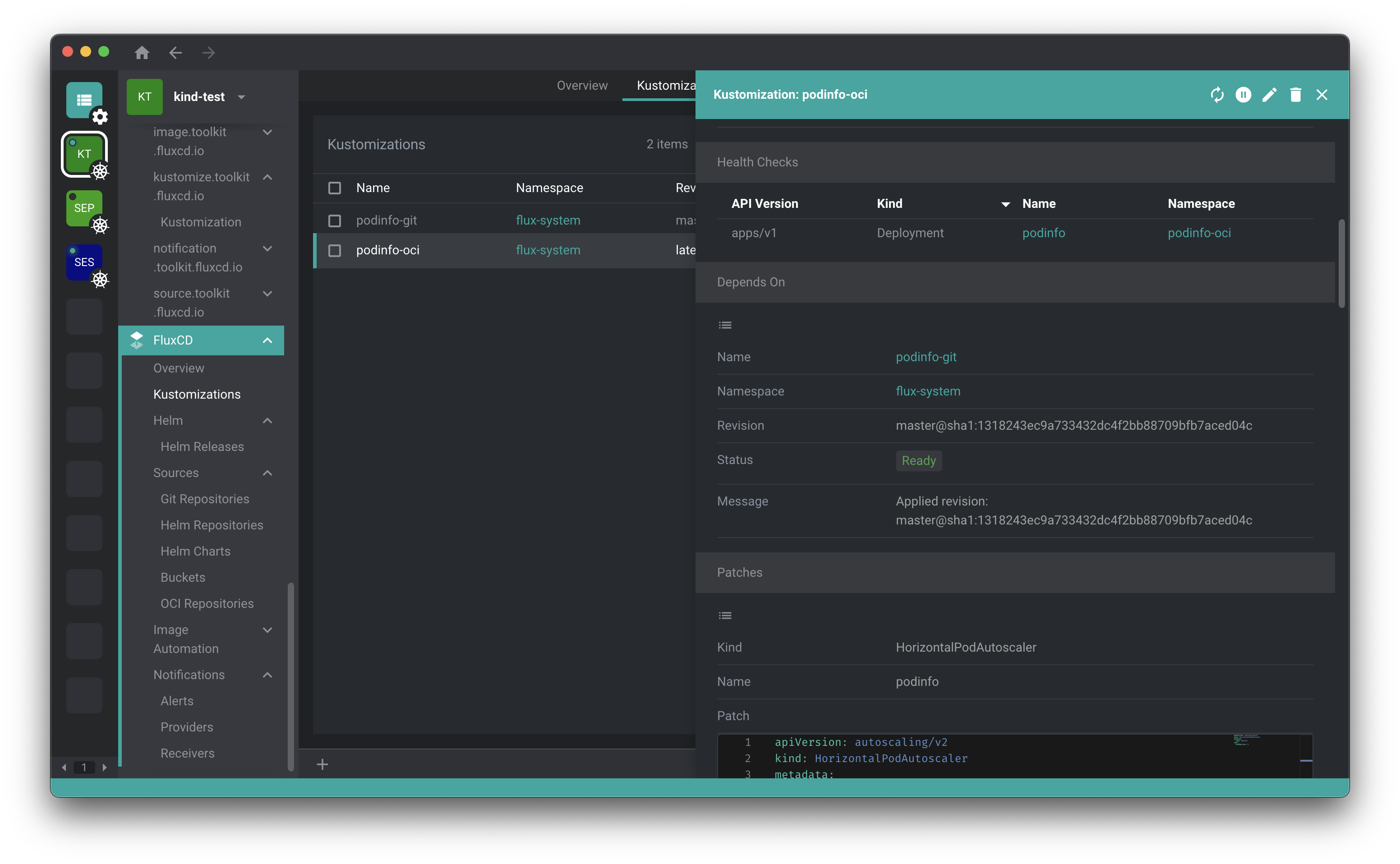
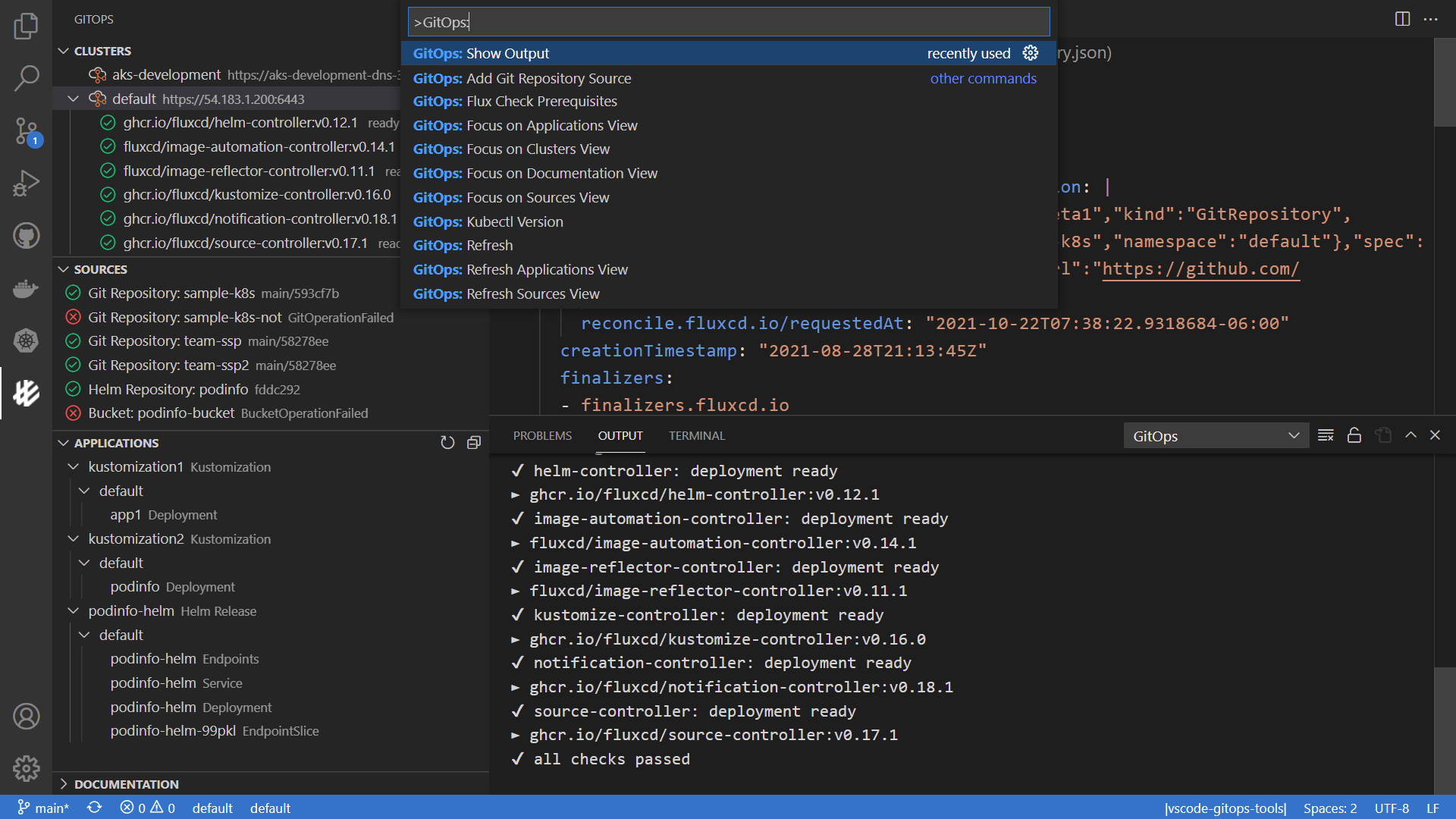
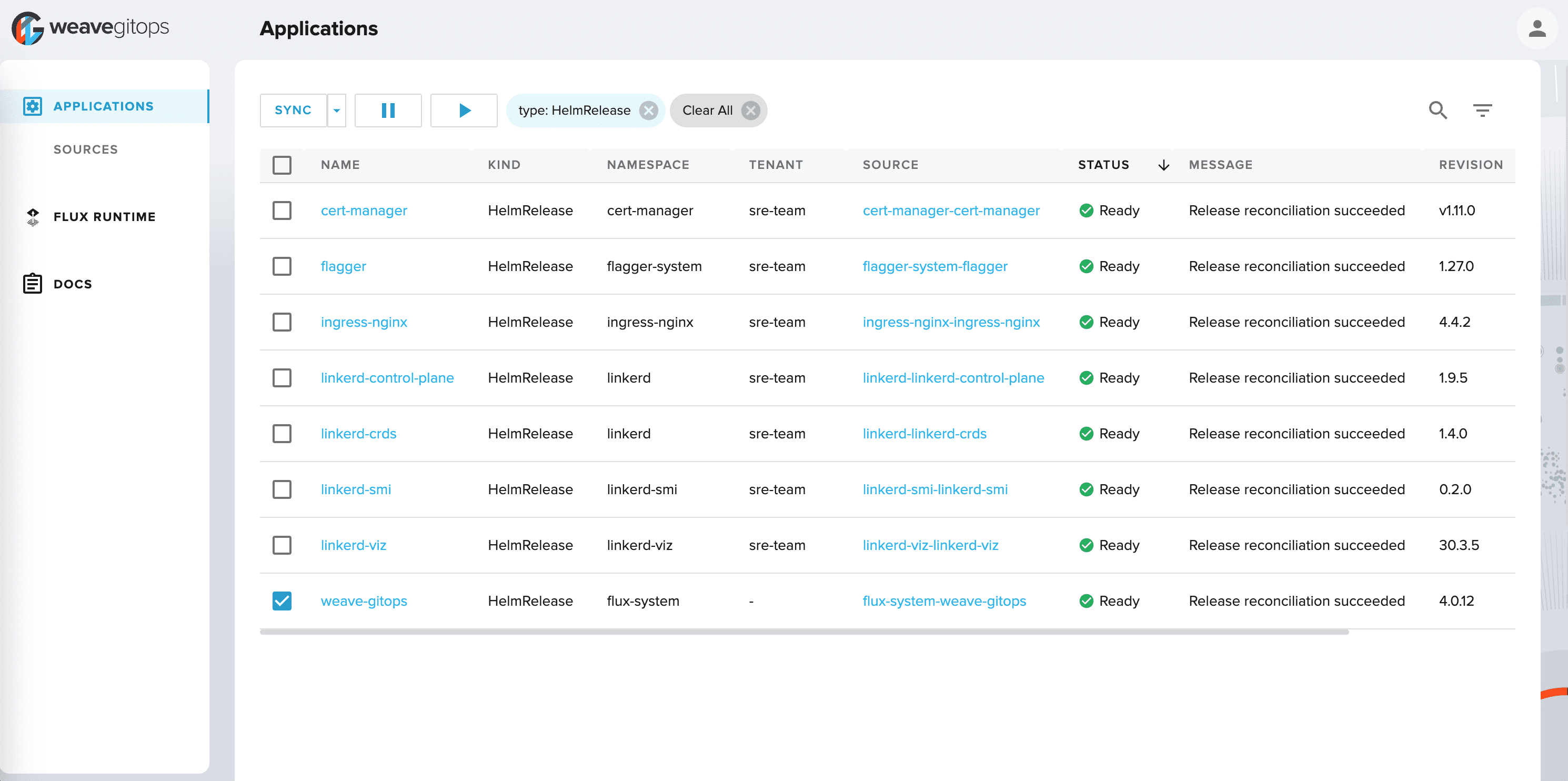
If you want to find out more about Flux UIs, check out our dedicated section.
| 🤝 Flux provides GitOps for both apps and infrastructure | Flux and Flagger deploy apps with canaries, feature flags, and A/B rollouts. Flux can also manage any Kubernetes resource. Infrastructure and workload dependency management is built in. |
| 🤖 Just push to Git and Flux does the rest | Flux enables application deployment (CD) and (with the help of Flagger) progressive delivery (PD) through automatic reconciliation. Flux can even push back to Git for you with automated container image updates to Git (image scanning and patching). |
| 🔩 Flux works with your existing tools | Flux works with your Git providers (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, can even use s3-compatible buckets as a source), all major container registries, fully integrates with OCI and all CI workflow providers. |
| 🔒 Flux is designed with security in mind | Pull vs. Push, least amount of privileges, adherence to Kubernetes security policies and tight integration with security tools and best-practices. Read more about our security considerations. |
| ☸️ Flux works with any Kubernetes and all common Kubernetes tooling | Kustomize, Helm, RBAC, and policy-driven validation (OPA, Kyverno, admission controllers) so it simply falls into place. |
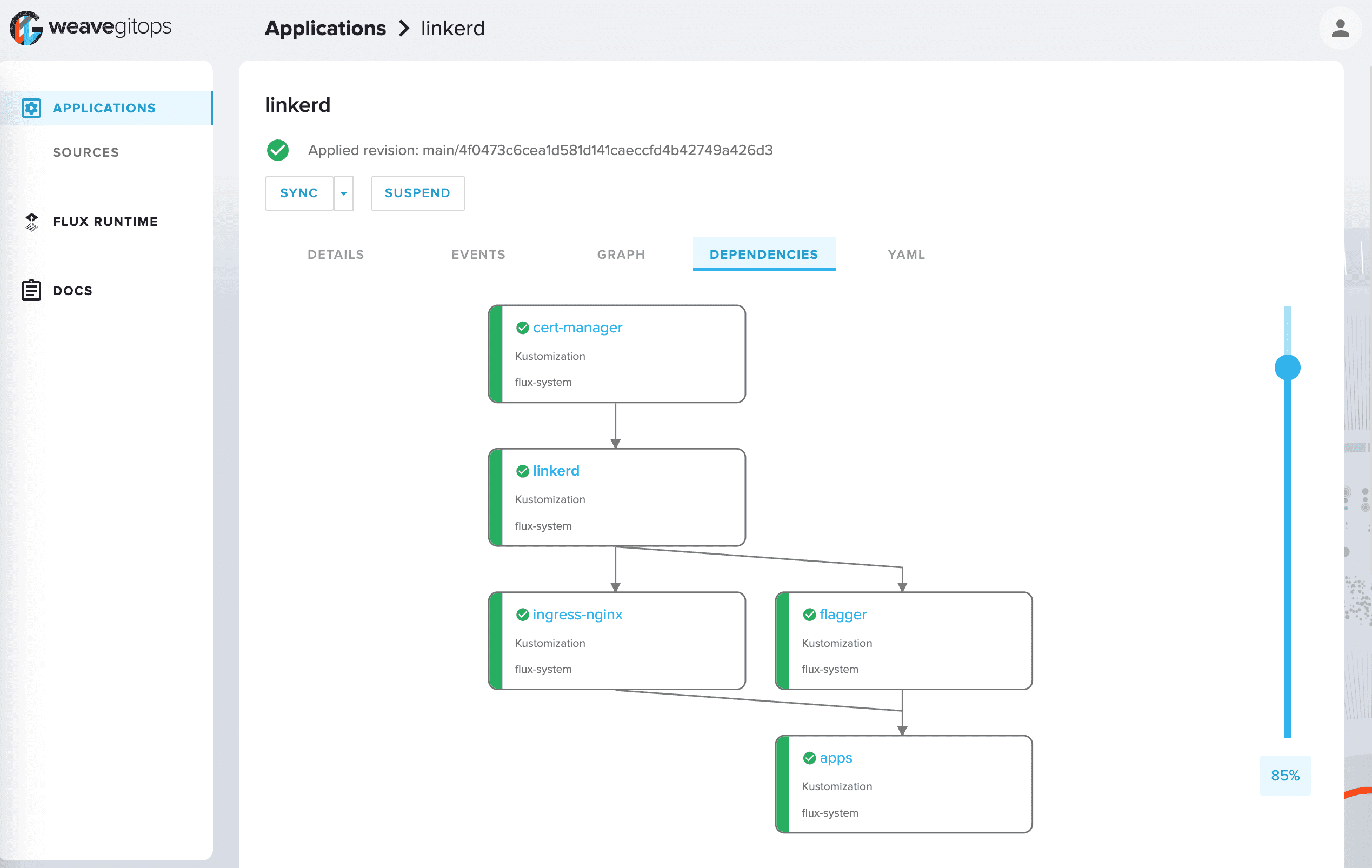
| 🤹 Flux does Multi-Tenancy (and “Multi-everything”) | Flux uses true Kubernetes RBAC via impersonation and supports multiple Git repositories. Multi-cluster infrastructure and apps work out of the box with Cluster API: Flux can use one Kubernetes cluster to manage apps in either the same or other clusters, spin up additional clusters themselves, and manage clusters including lifecycle and fleets. |
| ✨ Dashboards love Flux | No matter if you use one of the Flux UIs or a hosted cloud offering from your cloud vendor, Flux has a thriving ecosystem of integrations and products built on top of it and all have great dashboards for you. |
| 📞 Flux alerts and notifies | Flux provides health assessments, alerting to external systems, and external events handling. Just “git push”, and get notified on Slack and other chat systems. |
| 👍 Users trust Flux | Flux is a CNCF Graduated project and was categorised as “Adopt” on the CNCF CI/CD Tech Radar (alongside Helm). |
| 💖 Flux has a lovely community that is very easy to work with! | We welcome contributors of any kind. The components of Flux are on Kubernetes core controller-runtime, so anyone can contribute and its functionality can be extended very easily. |
Flux helps
Flux is based on a set of Kubernetes API extensions (“custom
resources”), which control how git repositories and other sources of
configuration are applied into the cluster (“synced”).
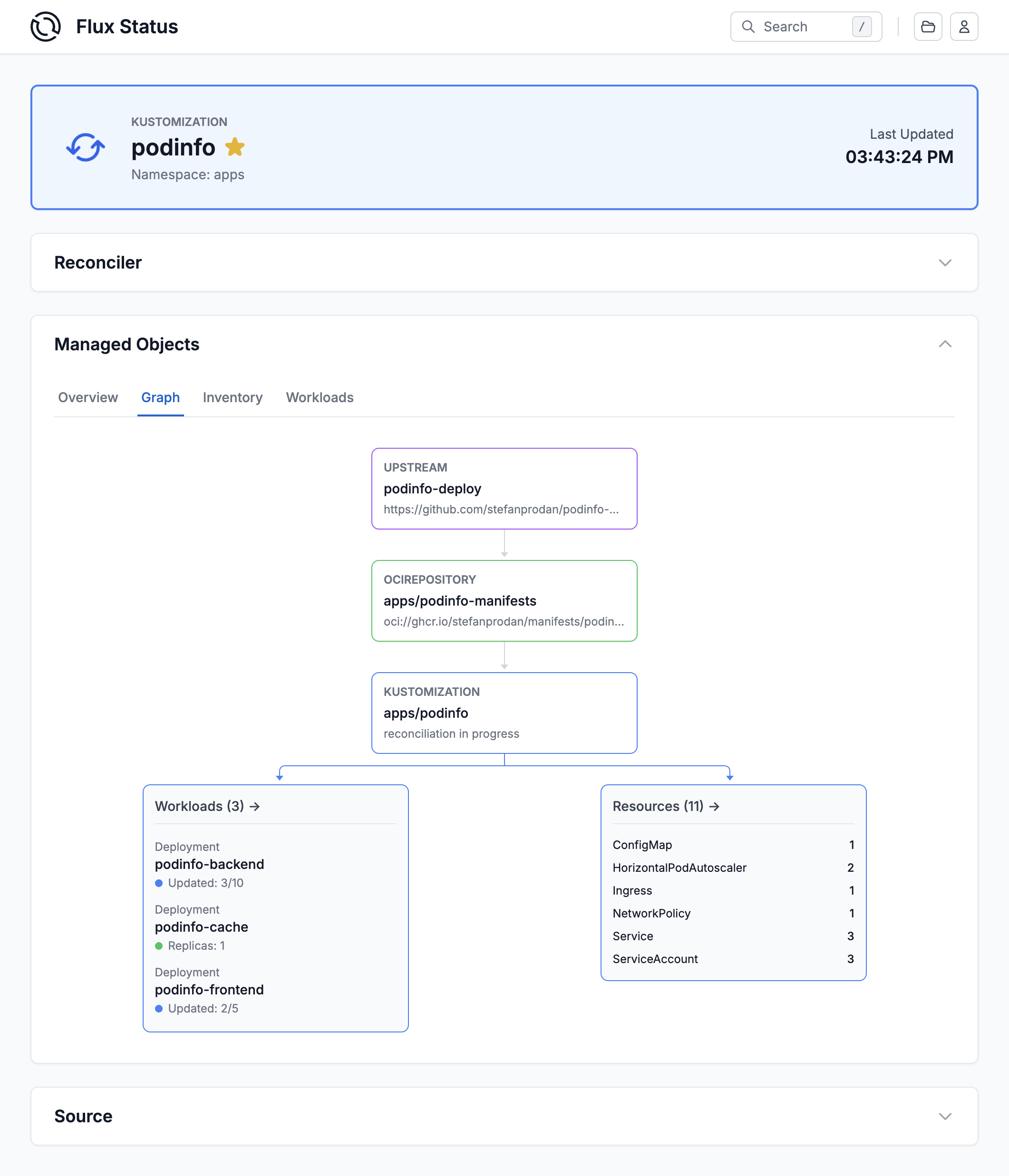
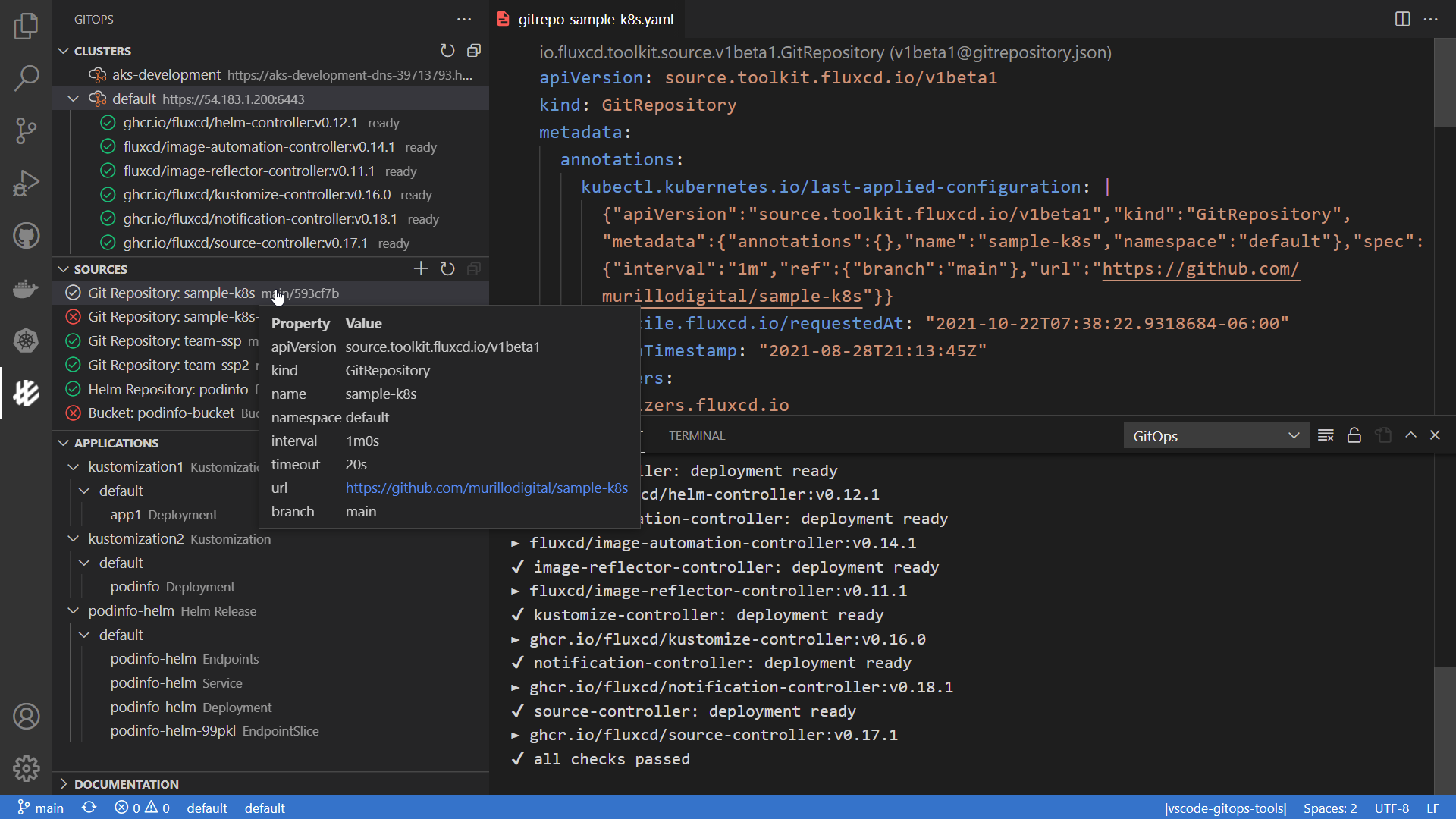
For example, you create a GitRepository object to mirror
configuration from a Git repository, then a Kustomization object to
sync that configuration.
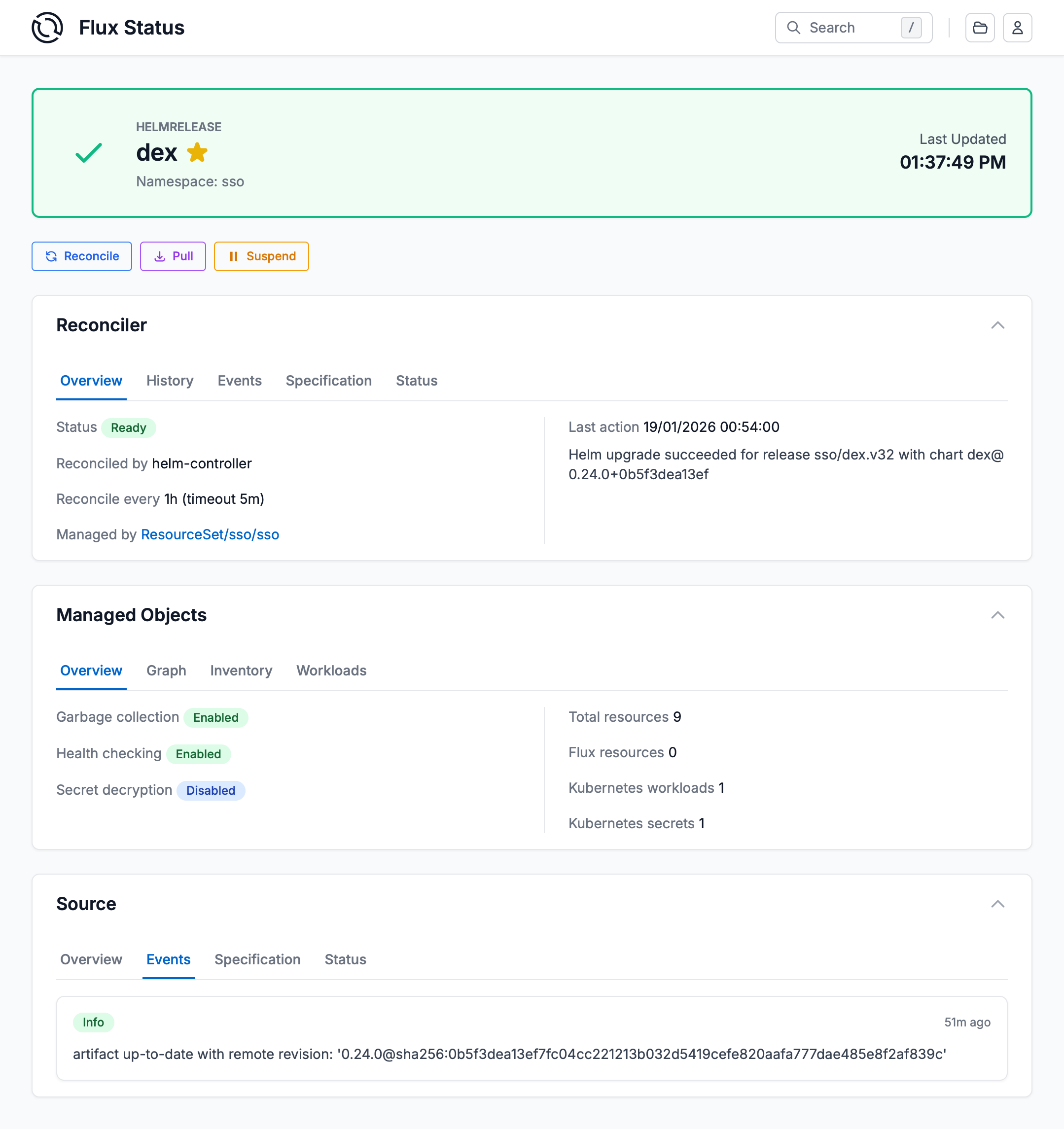
Flux works with Kubernetes’ role-based access control (RBAC), so you can lock down what any particular sync can change. It can send notifications to Slack and other like systems when configuration is synced and ready, and receive webhooks to tell it when to sync.
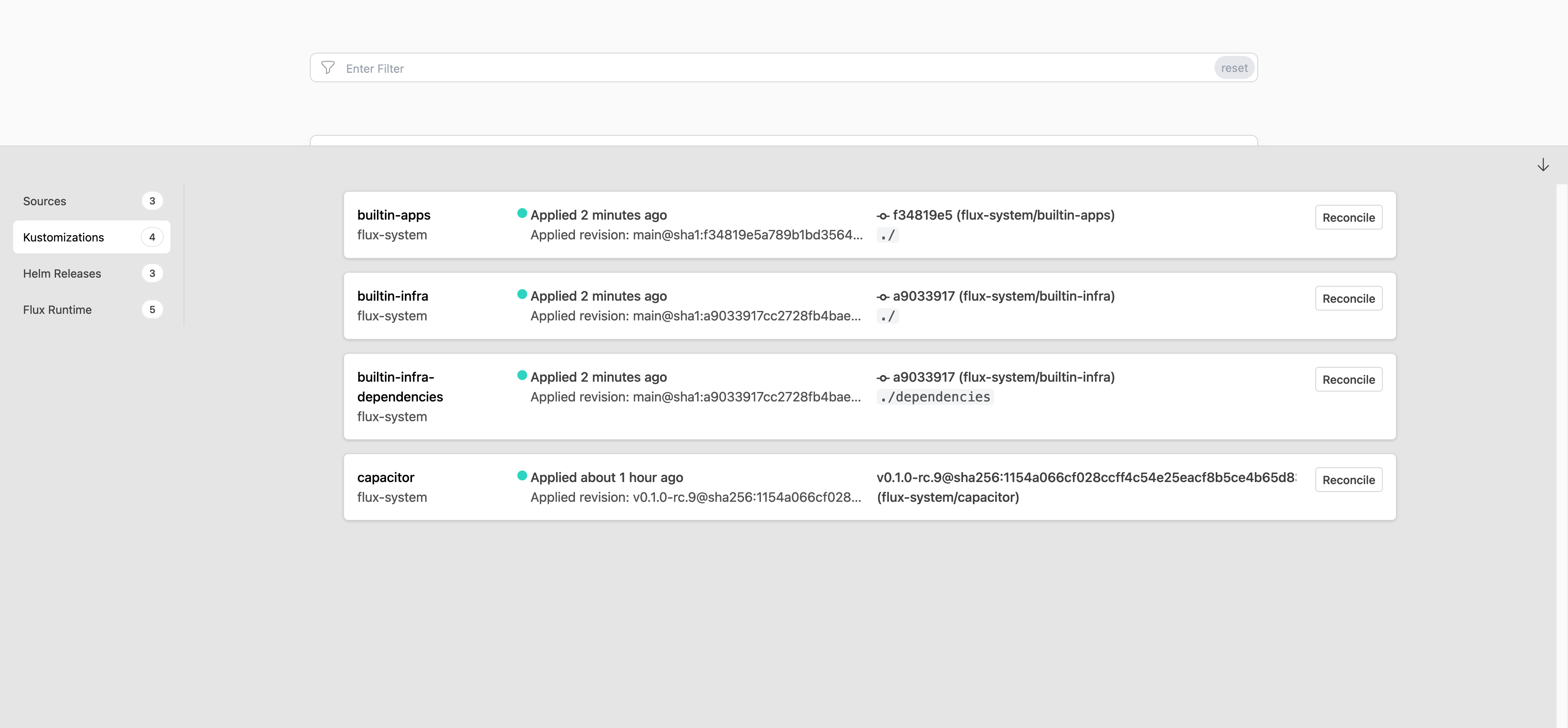
The flux command-line tool is a convenient way to bootstrap the
system in a cluster, and to access the custom resources that make up
the API.
flux CLI and running a couple of very simple commands,
you will have a GitOps workflow setup which involves a staging and a production cluster.If you should need help, please refer to our Support page.
Features:
Flux is constructed with the GitOps Toolkit components, which is a set of
for building Continuous Delivery on top of Kubernetes.
The GitOps Toolkit can be used individually by platform engineers who want to make their own continuous delivery system, and have requirements not covered by Flux.
Need help or want to contribute? Please see the links below. The Flux project is always looking for new contributors and there are a multitude of ways to get involved.
Check out our events calendar, both with upcoming talks you can attend or past events videos you can watch.
We look forward to seeing you with us!
Core Concepts of Flux.
Get Started with Flux.
How to install the Flux CLI and the Flux controllers.
Flux user guides.
How to configure authentication and authorization for the Flux integrations with external systems.
How to configure monitoring for Flux.
Flux use cases.
Documentation of the individual GitOps Toolkit components and their APIs.
The GitOps Toolkit development documentation.
The Flux Command-Line Interface documentation.
Flux cheatsheets.
Flux Security documentation.
Flux release documentation.
Flux and the GitOps Toolkit frequently asked questions.
How to use the Flux CLI in GitHub Actions workflows.
A narrative of the life of a commit as it relates to Flux components.
Migration guides for Flux v1 and Helm Operator users.